- Conditions
- DISI deformity
DISI deformity Dorsal intercalated segment instability
Introduction
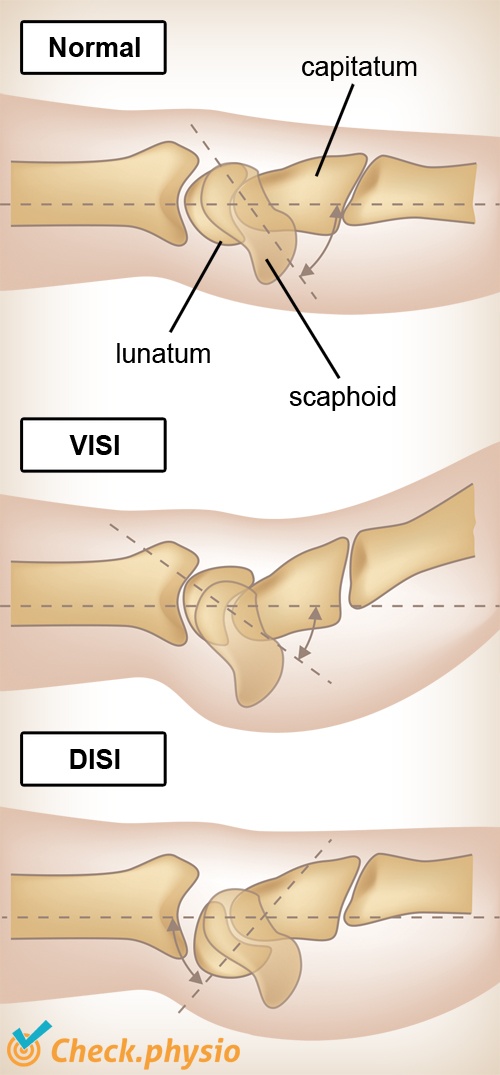
A DISI deformity is a condition in which there is a mutual change in position of two carpal bones in the wrist joint. This causes symptoms in the wrist area, particularly when extending the wrist.
In addition to DISI deformity, there is also VISI deformity (Volar Intercalated Segment Instability). However, this is much less common.
Description of the condition
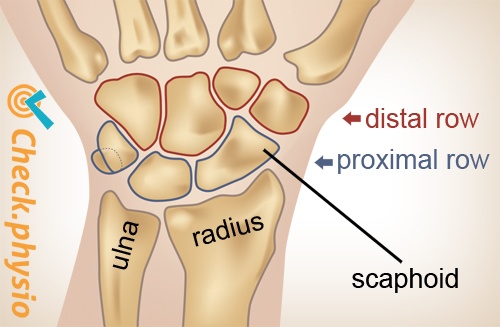
There are eight carpal bones in the wrist joint. They are divided into two imaginary rows that lie adjacent to each other and together they form the transition from the forearm to the hand. The row that lies adjacent to the forearm is called the 'proximal row'. The other row, located closer to the hand, is called the 'distal row'.
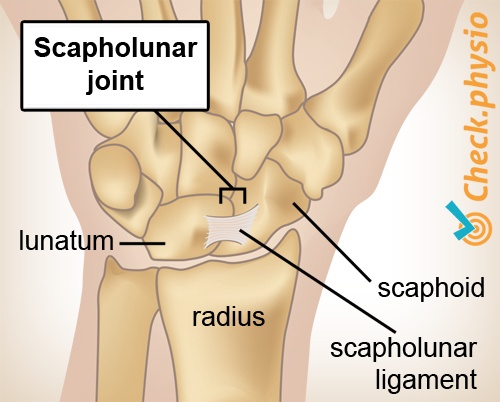
The carpal bones of the proximal row play a prominent role in DISI deformity. The lunate bone and the scaphoid bone are not positioned correctly in the wrist. This can cause damage to the ligaments. This results in instability of the scapholunate joint.
Cause and origin
Scapholunar instability can have many causes.
- A fall on an outstretched hand.
- (Congenital) joint laxity.
- Overloading through activities or prolonged walking on crutches.
- Frequent joint inflammation (arthritis).
- A scaphoid fracture.
Signs & symptoms
The most important symptoms include:
- Pain when extending the wrist.
- Loss of strength.
- Pressure pain on the scapholunar joint.
In addition, other symptoms can also occur, such as snapping or clicking during wrist movements and problems with gripping objects. In some cases a sudden, severe pain will shoot through the wrist. This can be associated with a crippling sensation.
Diagnosis
The healthcare professional asks in an interview about the complaints and how they arose. This is followed by a physical examination in which the hand and wrist are examined and some tests are performed.
In case of a suspected DISI deformity, additional investigation will often follow by means of MRI.
Treatment and recovery
Depending on the situation, interventions as physiotherapy, splint treatment or surgery can provide relief.
More info
You can check your symptoms using the online physiotherapy check or make an appointment with a physiotherapy practice in your area.
References
Nugteren, K. van & Winkel, D. (2006) Onderzoek en behandeling van de hand - het pols gewricht Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.