- Conditions
- Anterior cruciate ligament injury
Anterior cruciate ligament injury ACL injury
Introduction
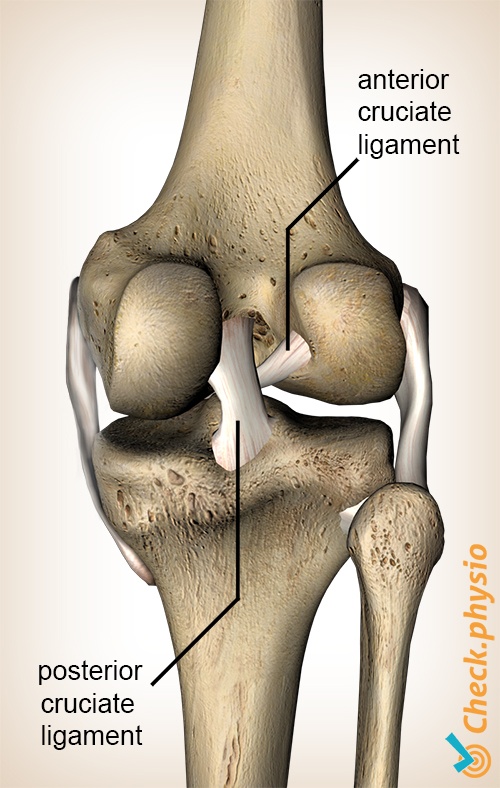
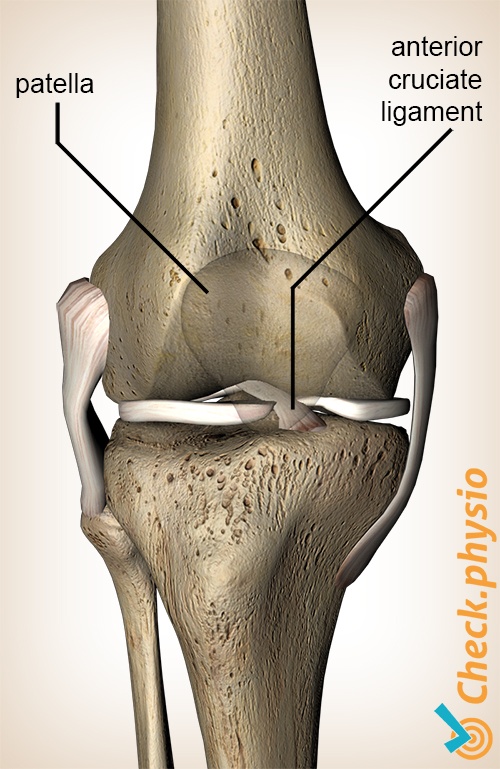
The anterior cruciate ligament is located in the middle of the knee. It is a strong structure that prevents the lower leg from moving too far forward in relation to the upper leg. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries have significant consequences, particularly for keen athletes.
Anterior cruciate ligament injuries are relatively common in sports where the knee can easily twist. Examples include football, rugby, basketball, handball, korfball and skiing.
Description of the condition
There are two cruciate ligaments in the knee: the anterior and posterior cruciate ligament. Both connect the upper leg to the lower leg and play an important role in maintaining the stability of the knee joint.
The anterior cruciate ligament prevents the lower leg from moving too far forward in relation to the upper leg. It also limits excessive rotational movements of the knee. If an anterior cruciate ligament injury occurs, these movements are no longer limited sufficiently, making the knee unstable. The ligament can tear partially or completely.
Often the anterior cruciate ligament is not the only affected structure. Meniscus injury, ligament injury and cartilage injury are often seen with anterior cruciate ligament injury.
Cause and origin
The injury usually occurs at a clearly defined moment. Often with an unexpected movement of the body in which the flexed knee is twisted. The patient feels something 'pop' or 'snap' in the knee and experiences severe pain.
The knee becomes swollen a short time after the cruciate ligament tears. It then becomes difficult to bear weight on the knee and the knee feels unstable. The patient feels as if the knee cannot support him/her.
Signs & symptoms
Pain is not always a specific characteristic of anterior cruciate ligament injury. The pain is usually caused by damage to the surrounding structures. If the knee is still swollen several weeks after the injury, this is often a symptom of an unstable knee. An incomplete tear of the cruciate ligament often results in more pain than a complete tear.
The instability of the knee can be felt during exercise, but also during more normal activities such as walking up and down stairs, walking on uneven surfaces or getting out of a vehicle.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is usually made based on the patient's story about the moment that the injury occurred and on the physical examination. If this supports the theory of anterior cruciate ligament rupture, an arthroscopy (keyhole surgery) will be performed in many cases.
Treatment and recovery
The young, active patient, who exercises a lot and has a feeling of instability as a result of a cruciate ligament rupture is more likely to have surgery. During the procedure, the torn cruciate ligament is replaced by a new cruciate ligament. This can be from a harvested tendon obtained from elsewhere in the body or an artificial one. A part of the patellar tendon or the hamstring tendon is often used for this purpose.
Patients who are not active, who are older and who do not exercise vigorously are less likely to have surgery. The same applies to cruciate ligaments that are only partially ruptured. Exercises to strengthen the muscles and provide stability can be enough to alleviate the symptoms.
More info
You can check your symptoms using the online physiotherapy check or make an appointment with a physiotherapy practice in your area.
References
Nugteren, K. van & Winkel, D. (2008) Onderzoek en behandeling van de knie Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Brooijmans, F., Huiberts, L., Hekking, J. & Lataster, A. (2011) Kan de fysiotherapeut acute knieletsels adequaat diagnosticeren Physios: 2011-1-5.
Verhaar, J.A.N. & Linden, A.J. van der (2005) Orthopedie Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.