- Conditions
- Transient synovitis
Transient synovitis Inflammation of the hip in children / toxic synovitis / coxitis fugax
Introduction
Transient synovitis or coxitis fugax is the most common hip condition affecting children aged 3 to 10 years. The hip joint is irritated, causing the child to start limping suddenly, or not wanting to walk or stand at all. The abnormality is more common in boys than in girls.
The natural progression is favourable. The name of the condition actually describes this already. 'Fugax' means 'brief' or 'transient'.
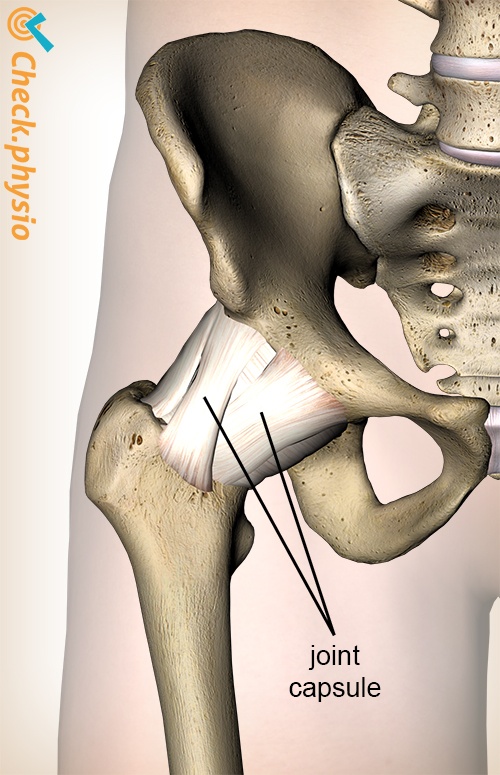
Description of the condition
Transient synovitis is a benign irritation of the hip joint. An inflammatory reaction occurs in the joint capsule of the hip. The disease almost always presents only on one side.
Cause and origin
The cause is unknown. It is noteworthy that almost half of all cases are preceded by symptoms of a (viral) infection.
Signs & symptoms
- Pain in the hip region (groin), the thigh and sometimes the knee.
- The gait is disrupted and the child limps.
- Sometimes the child does not want to stand or walk at all.
- Sideways elevation and rotational movements of the hip are limited.
- The child is usually not sick.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is confirmed by means of the physical examination and radiological examination. An ultrasound will reveal fluid in the hip joint. If there is any uncertainty about the diagnosis, a joint puncture is performed to remove fluid from the joint for laboratory testing.
Treatment and recovery
The treatment consists of rest. The child is not allowed to walk temporarily, but usually does not need to be admitted to hospital. The symptoms persist for a maximum of 1 to 2 weeks.
More info
You can check your symptoms using the online physiotherapy check or make an appointment with a physiotherapy practice in your area.
References
Verhaar, J.A.N. & Linden, A.J. van der (2005) Orthopedie Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
